Consider the possibility that people could make the tuberculosis antibody considerably more dominant, not by adjusting the fixings, yet just by changing the manner in which it is given to individuals. It would help avert the disease that murders a greater number of individuals consistently than some other organism.
Tuberculosis is brought about by a bacterium, called Mycobacterium tuberculosis, which causes a lung disease that advances gradually however can decimate the lungs if not treated. In spite of the fact that we probably won’t consider it time and again here in the United States, it stays a significant executioner around the world.
In 2018 alone, there were 10 million new instances of dynamic TB and practically 1.5 million passings from TB contaminations. What makes the malady especially slippery is that since manifestations are delayed to show and can look like different sicknesses, it takes quite a while before individuals with TB are analyzed and given treatment.
Be that as it may, until an individual with TB gets treated with drugs, they can give it to others – and this bacterium spreads quick through hacking, sniffling, and in any event, singing.
People may be astounded to discover that a large portion of the individuals who kick the bucket from TB were really inoculated as a child, utilizing an antibody called Bacille Calmette-Guerin (BCG). BCG has been utilized for just about 100 years and is a live however injured form of a comparative bacterium to the one that causes TB.
This antibody is entirely great at counteracting specific sorts of TB in kids, however not young people or grown-ups. Their group here in Pittsburgh together with associates at the National Institutes of Health have made sense of a superior method to control this immunization to counteract this overwhelming infection – which frequently influences the least fortunate individuals on the planet.
TB in mice and monkeys
They was initially prepared as a microbiologist, considering microorganisms that cause malady, and later built up an enthusiasm for how the body’s insusceptible framework fends off diseases. Joining their interests for microbiology and immunology, they started researching tuberculosis just about 30 years prior.
They began their very own lab at the University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine with the objective of understanding TB infection and how people may forestall it.
They began by utilizing mice to consider TB. In any case, at that point, 20 years back, they started utilizing monkeys and found that monkeys build up a similar kind of TB infection that people do. Examining TB in monkeys was a leap forward that empowered me to start the quest for new antibodies against this fatal ailment.
TB is such a captivating sickness and has been causing ailment in people for a large number of years. Anthropologists have found, for instance, tuberculosis in Egyptian mummies. It taints about all well evolved creatures.
However, despite the fact that the reason for TB has been known since the late 1800s, it is as yet not clear why a few people can smother the contamination and not become wiped out while others are increasingly helpless and create ailment.
They needed to utilize their comprehension of this convoluted bacterium to discover progressively successful approaches to avoid the infection.
Another immunization system
Their associate Robert Seder, an immunization master at the National Institutes of Health, had found that conveying an intestinal sickness antibody legitimately into the circulatory system, through a vein, was substantially more compelling than some other course of conveyance, for example, the skin or muscle, and was a greatly improved approach to avert the ailment.
Together, people chose to attempt a comparable methodology with TB utilizing the current BCG immunization. People immunized monkeys with BCG by infusing the immunization under the skin (the standard course for babies), by aerosolizing the antibody and showering it legitimately into the lungs, or infusing it straightforwardly into the blood utilizing an IV.
Following two months we found that when the immunization was conveyed by means of IV, the quantities of particular safe cells, called T cells, which can perceive and kill the microbes, expanded by 100-crease in the lungs. At that point, months after the fact, people presented the monkeys to M. tuberculosis.
Unvaccinated monkeys created extreme TB ailment inside a couple of months. BCG managed through the skin or into the lungs gave a smidgen of assurance, however the monkeys still had indications of TB.
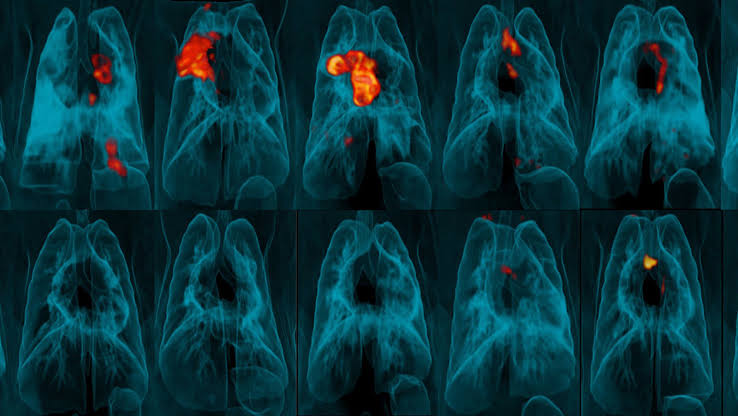
The IV immunization gave unimaginable assurance. In the greater part of the creatures, there were no M. tuberculosis microorganisms in the whole monkey. People likewise utilized particular imaging, called PET-CT, and indicated that the lungs of the vast majority of these monkeys were liberated from any illness. This implies BCG immunization forestalled TB contamination and malady when given intravenously.
This is an energizing leap forward in the field of TB, since most immunizations tried in any models give generally constrained insurance. On the off chance that people can make sense of how BCG IV forestalls M. tuberculosis contamination, people might be on the way to building up another antibody for people.
In spite of the fact that people have far to go before it is prepared for people, the exercises people gain from the BCG IV studies will be basic in growing new TB immunizations and, people trust, sparing a large number of lives.
Disclaimer: The views, suggestions, and opinions expressed here are the sole responsibility of the experts. No Times World USA journalist was involved in the writing and production of this article.